Violin
The violin is the primary member of the violin family. It has four strings tuned in perfect fifths, and is played rested on the shoulder while using a bow. Music for the violin is written using the treble clef. The violin was first developed by instrument makers in Northern Italy who drew upon earlier Middle Eastern bowed instruments as inspiration. The violin is a versatile melodious instrument, which is also easy to transport due to its small size. As such, the violin is used in many genres of music including classical, country and bluegrass, Hungarian and gypsy, Celtic, pop and jazz.
- The History of the Violin
- Types of Violins
- Parts of the Violin
- How to Tune the Violin
- How to String a Violin
- How to Play the Violin
- Articles about the Violin
History of the Violin
Read the full article: History of the Violin
The violin was developed in Northern Italy in the mid-16th century. It is believed that the violin was first designed by Italian instrument craftsmen who crafted the violin family instruments after seeing similar early Middle Eastern and Byzantine bowed stringed instruments. A number of different bowed stringed instruments were developed in Europe in the 16th century, inspired by these Middle Eastern and Byzantine instruments, which has made it relatively difficult to determine the early history of the instrument. The violin became popular with both low and high-class musicians due to its relatively low cost and accessibility. The violin underwent some extensive changes between the 16th and 19th centuries to adjust the tonal quality of the instrument. Violins can now be mass-produced, however many professional luthiers still hand-craft the instruments. Older violins are still sought after for their superior tone.
For more information on the history of the violin, see our History of the Violin article.
Types
Read the full article: Types of Violins
The violin has had an extensive history, which so far has spanned over 450 years. As such, the violin has various different forms from specific time periods, as well as variations meant to enhance different playing styles and genres (such as a flatter bridge to aid double-stopping on the fiddle-violin, commonly used in country music). Violins also come in different sizes, so that children can learn the violin. Modern violins can produce sound either electrically or acoustically. Sometimes on modern instruments the range of the violin is extended to include the lower C-string, which effectively combines the ranges of both the violin and its sister instrument; the viola.
For more information on different types of violin, see our Types of Violins article.
Parts of the Violin
Read the full article: Parts of the Violin
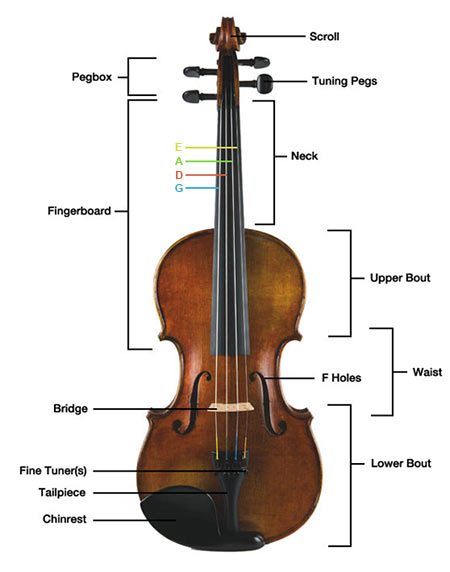
To learn more about the different parts of the violin, see our Parts of the Violin article.
How to Tune the Violin
Read the full article: How to Tune the Violin
The violin has four strings which are tuned in fifths. The scientific pitch of the strings from lowest to highest is: G3, D4, A4, and E5.
| Standard Violin Tuning - A4(Hz): 440 | ||||
| String | Scientific pitch | Helmholtz pitch | Semitones from Middle C | Frequency (Hz) |
| G | G3 | g | -5 | 196.00 |
| D | D4 | d′ | 2 | 293.66 |
| A | A4 | a′ | 9 | 440.00 |
| E | E5 | e′′ | 16 | 659.26 |
Online Violin Tuners
Online Violin Tuner - Tune a violin using the standard GDAE tuning.
Online Instrument Tuner - Tune a violin by using the microphone on your computer.
For more information on how to tune the violin, see our How to Tune the Violin article. This article contains information on how best to tune your violin, and tips to make tuning your violin easy!
How to String a Violin
Read the full article: How to String a Violin
Violin strings can sometimes snap when tuning. They can also start to unwind, which causes a 'fuzzy' or 'buzzing' sound when you play. If you have an old violin that has not been played for a while, the strings may lose their flexibility and quality of tone. If you have strings that have been regularly played, then the strings can become dirty from the natural oils secreted by the fingers and from rosin, which can build up a sticky residue on the surface of the string between the bridge and the fingerboard. Restringing a violin can be a daunting task for beginners, but with the right information and some practice, soon you will be restringing like a pro!
To learn how to restring a violin, see our How to String a Violin article.
How to Play the Violin
Read the full article: How to Play the Violin
The violin is held under the chin while bowed, and occasionally plucked. Orchestral and chamber violinists sit while playing, taking care to keep their backs straight so to avoid shoulder and back strain. Soloist violinists usually stand while playing which allows the player to have more room to move. Violinists read music written on the treble clef. Advanced players have a playing range on the violin of four octaves, which can also be further extended using natural and artificial harmonics.
To learn more about how to play the violin, see our How to Play the Violin article.
Articles about the Violin
 Violin Buyers Guide
Violin Buyers Guide
What should you look for when you buy a violin? This article gives a run-down on the things you really need to know before buying (or selling) your violin.
 Violin Accessory Guide
Violin Accessory Guide
From shoulder rests to rosin, chin rests to mutes, this article explains all about violin accessories, and what to watch out for when you buy them.
 How to Maintain a Violin
How to Maintain a Violin
How do you get the best tone out of your violin? By making sure you maintain it well! This article will tell you all you need to know to keep your violin singing (and looking) beautiful.









good
:)
I really like that it shows us that the violin example.
Interesting.
It's completely unthinkable that one wrote "this is not helpful at all.". In fact it is so interesting.
Emeraude
This is really good info I love it🤗
These are good things to know people even if you have played a violin for years it’s still nice to have a refresher. This is helpful if this is the info you’re looking for so to all the people who say it’s not then you’re looking in the wrong place buddy chum pal.
These are good things to know people even if you have played a violin for years it’s still nice to have a refresher. This is helpful if this is the info you’re looking for so to all the people who say it’s not then you’re looking in the wrong place buddy chum pal.
this is not helpful at all.
this is not helpful at all.
I really like that it shows us that the violin example.
:)
Good information!
this was awsome
this was awsome
I love playing and I want to get better at playing
You think so Kalee Charisma
You think so Kalee Charisma
accordare
Not help full
What is this f***ing CRAP
this is pretty good info thanks!